Updating A Table Of Contents In Microsoft Word
Update the data in a database. This article explains how to update existing data. Microsoft Office Access 2. Data Collection feature. As you proceed, remember that updating data is not the same process as entering new data. Gta Sa Driver Mod 1.3. For information about entering new data in a database, see the article Add one or more records to a database. Updating A Table Of Contents In Microsoft Word' title='Updating A Table Of Contents In Microsoft Word' />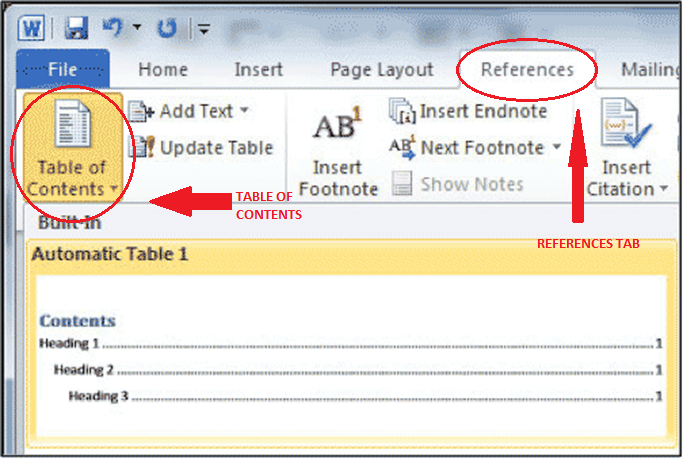 In this article. How database design affects updating. How data types affect updating. How table field properties affect updating. Use a form to update data. Use a datasheet to update data. Use an update query to change existing data. Need to set up a table of contents quickly These templates will help you get the job done in a flash. Need User Guide templates to create user guides, user manuals, getting started guides or other types of technical documents Download samples here. Use an append query to add records to tables. Use Data Collection to update records. Use cascading updates to change primary and foreign key values. How database design affects updating. Read this section if you are new to Access or unfamiliar with the concepts behind relational databases. Large updates become much easier to perform when you understand some of the basic principles of database design. An Access database is not a file in the same sense as a Microsoft Office Word 2. Microsoft Office Power. Point 2. 00. 7 slide deck. Instead, a typical Access database is a a collection of tables, plus a set of objects built around those tables forms, reports, queries, and so on. In addition, those objects must adhere to a set of design principles or the database will either work poorly or fail altogether. In turn, those design principles affect how you enter data. Remember these facts about database objects and design as you proceed. With a few exceptions such as a type of list called a value list, Access stores all data in one or more tables. The number of tables depends on the design and complexity of the database. Although you may view or update the data in a form, a report, or in the results returned by a query, Access stores the data only in tables. Each table should store data for a single issue, category, or purpose. Updating A Table Of Contents In Microsoft Word' title='Updating A Table Of Contents In Microsoft Word' />This chapter shows how fields work in Microsoft Word 2013 and how to insert them. Youll also find out how to use form fields to create forms. Microsoft Word 2010 A Users Manual for Professors in the Humanities iii Table of Contents 1. Basics 1. 1 Introduction 1 1. Features of the Microsoft. Complex Documents Microsoft Word Intermediate Users Guide. Tables of Contents generated by Word are fields. Specifically, a TOC field. Example. This TransactSQL example updates a partial value in DocumentSummary, an nvarcharmax column in the Document table in the AdventureWorks database. Updating A Table Of Contents In Microsoft Word' title='Updating A Table Of Contents In Microsoft Word' />For example, a table of business contact information should not contain sales information. If it does, finding the correct information can become difficult, if not impossible. Each of the fields in a table should accept only one type of data. For example, you should not store notes in a field set to accept numbers. If you try to enter text in such a field, Access displays an error message. With one exception, the fields in a record should accept only one value. For example, a properly designed database will prevent you from entering more than one address in an address field. This is in contrast to Microsoft Office Excel 2. However, Office Access 2. You use multivalued fields to attach multiple pieces of data to a single record, and to create lists that accept multiple values. For example, you can attach a text file, a Office Power. Point 2. 00. 7 slide deck, and any number of images to a record in your database. You can also create a list of names and select as many of those names as needed. The use of multivalued fields may seem to break the rules of database design because you can store more than one piece of data per table field, but it actually doesnt, because Access enforces the rules behind the scenes, by storing the data in special, hidden tables. The following links take you to articles that provide more information about the subjects and features discussed in this section. Top of Page. How data types affect updating. Read this section if you are new to Access or unfamiliar with the concepts behind relational databases. Large updates become much easier to perform when you understand some of the basic principles of database design. When you design a database table, you select a data type for each of the fields in that table, a process that helps ensure more accurate data entry. For example, suppose you specify the Number data type for a field because you need to calculate sales figures. If someone tries to enter text in that field, Access displays an error message and will not let that user save the changed record, a step that helps protect your figures. Show me how to view data types. Access now provides two ways to view the data types for a table field. You can use the commands on the Datasheet tab, or you can open the table in Design view. The following sets of steps explain how to use both techniques. View data types by using commands on the Datasheet tab. In the Navigation Pane, double click the table that you want to use. Click the field that you want to investigate. On the Datasheet tab, in the Data Type Formatting group, click the down arrow for the Data Type list to view the data type set for the field. View data types in Design view. In the Navigation Pane, right click the table and click Design View on the shortcut menu. Access opens the table in the design grid, and the upper section of the grid shows the name and data type of each table field. The data type set for each table field provides the first level of control over what you can and cannot enter into a field. In some cases, a data type setting prevents you from entering any information at all. The following table lists the data types that Office Access 2. Data type. Effect on data entry. Text. Text fields accept either text or numeric characters, including delimited lists of items. A text field accepts a smaller number of characters than does a Memo field from 0 to 2. In some cases, you can use conversion functions to perform calculations on the data in a Text field. Memo. You can enter large amounts of text and numeric data in this type of field. Also, if the database designer sets the field to support rich text formatting, you can apply the types of formatting that you normally find in word processing programs, such as Office Word 2. For example, you can apply different fonts and font sizes to specific characters in your text, and make them bold or italic, and so on. You can also add Hypertext Markup Language HTML tags to the data. For more information about using rich text formatting in a Memo field, see the article Format data in rows and columns. Like Text fields, you can also run conversion functions against the data in a Memo field. Number. You can enter only numbers in this type of field, and you can perform calculations on the values in a Number field. DateTime. You can enter only dates and times in this type of field. Depending on how the database designer sets the field, you may encounter these conditions If the database designer set an input mask for the field a series of literal and placeholder characters that appear when you select the field, you must enter data in the spaces and the format that the mask provides. For example, if you see a mask such as MMMDDYYYY, you must type a date in that format in the spaces provided for example, Oct 1. You cannot type a full month name such as July, or a two digit year value. If the designer did not create an input mask to control how you enter a date or time, you can enter the value using any valid date or time format. For example, you can type 1. Oct. 2. 00. 6, 1. October 1. 1, 2. 00. The database designer might apply a display format to the field. In that case, if not input mask is present, you can enter a value in almost any format, but Access displays the dates in accordance with the display format. For example, you can type 1. Oct 2. 00. 6. For more information about input masks, see the article Format data in rows and columns. Currency. You can enter only currency values in this type of field. Also, you do not have to manually enter a currency symbol.
In this article. How database design affects updating. How data types affect updating. How table field properties affect updating. Use a form to update data. Use a datasheet to update data. Use an update query to change existing data. Need to set up a table of contents quickly These templates will help you get the job done in a flash. Need User Guide templates to create user guides, user manuals, getting started guides or other types of technical documents Download samples here. Use an append query to add records to tables. Use Data Collection to update records. Use cascading updates to change primary and foreign key values. How database design affects updating. Read this section if you are new to Access or unfamiliar with the concepts behind relational databases. Large updates become much easier to perform when you understand some of the basic principles of database design. An Access database is not a file in the same sense as a Microsoft Office Word 2. Microsoft Office Power. Point 2. 00. 7 slide deck. Instead, a typical Access database is a a collection of tables, plus a set of objects built around those tables forms, reports, queries, and so on. In addition, those objects must adhere to a set of design principles or the database will either work poorly or fail altogether. In turn, those design principles affect how you enter data. Remember these facts about database objects and design as you proceed. With a few exceptions such as a type of list called a value list, Access stores all data in one or more tables. The number of tables depends on the design and complexity of the database. Although you may view or update the data in a form, a report, or in the results returned by a query, Access stores the data only in tables. Each table should store data for a single issue, category, or purpose. Updating A Table Of Contents In Microsoft Word' title='Updating A Table Of Contents In Microsoft Word' />This chapter shows how fields work in Microsoft Word 2013 and how to insert them. Youll also find out how to use form fields to create forms. Microsoft Word 2010 A Users Manual for Professors in the Humanities iii Table of Contents 1. Basics 1. 1 Introduction 1 1. Features of the Microsoft. Complex Documents Microsoft Word Intermediate Users Guide. Tables of Contents generated by Word are fields. Specifically, a TOC field. Example. This TransactSQL example updates a partial value in DocumentSummary, an nvarcharmax column in the Document table in the AdventureWorks database. Updating A Table Of Contents In Microsoft Word' title='Updating A Table Of Contents In Microsoft Word' />For example, a table of business contact information should not contain sales information. If it does, finding the correct information can become difficult, if not impossible. Each of the fields in a table should accept only one type of data. For example, you should not store notes in a field set to accept numbers. If you try to enter text in such a field, Access displays an error message. With one exception, the fields in a record should accept only one value. For example, a properly designed database will prevent you from entering more than one address in an address field. This is in contrast to Microsoft Office Excel 2. However, Office Access 2. You use multivalued fields to attach multiple pieces of data to a single record, and to create lists that accept multiple values. For example, you can attach a text file, a Office Power. Point 2. 00. 7 slide deck, and any number of images to a record in your database. You can also create a list of names and select as many of those names as needed. The use of multivalued fields may seem to break the rules of database design because you can store more than one piece of data per table field, but it actually doesnt, because Access enforces the rules behind the scenes, by storing the data in special, hidden tables. The following links take you to articles that provide more information about the subjects and features discussed in this section. Top of Page. How data types affect updating. Read this section if you are new to Access or unfamiliar with the concepts behind relational databases. Large updates become much easier to perform when you understand some of the basic principles of database design. When you design a database table, you select a data type for each of the fields in that table, a process that helps ensure more accurate data entry. For example, suppose you specify the Number data type for a field because you need to calculate sales figures. If someone tries to enter text in that field, Access displays an error message and will not let that user save the changed record, a step that helps protect your figures. Show me how to view data types. Access now provides two ways to view the data types for a table field. You can use the commands on the Datasheet tab, or you can open the table in Design view. The following sets of steps explain how to use both techniques. View data types by using commands on the Datasheet tab. In the Navigation Pane, double click the table that you want to use. Click the field that you want to investigate. On the Datasheet tab, in the Data Type Formatting group, click the down arrow for the Data Type list to view the data type set for the field. View data types in Design view. In the Navigation Pane, right click the table and click Design View on the shortcut menu. Access opens the table in the design grid, and the upper section of the grid shows the name and data type of each table field. The data type set for each table field provides the first level of control over what you can and cannot enter into a field. In some cases, a data type setting prevents you from entering any information at all. The following table lists the data types that Office Access 2. Data type. Effect on data entry. Text. Text fields accept either text or numeric characters, including delimited lists of items. A text field accepts a smaller number of characters than does a Memo field from 0 to 2. In some cases, you can use conversion functions to perform calculations on the data in a Text field. Memo. You can enter large amounts of text and numeric data in this type of field. Also, if the database designer sets the field to support rich text formatting, you can apply the types of formatting that you normally find in word processing programs, such as Office Word 2. For example, you can apply different fonts and font sizes to specific characters in your text, and make them bold or italic, and so on. You can also add Hypertext Markup Language HTML tags to the data. For more information about using rich text formatting in a Memo field, see the article Format data in rows and columns. Like Text fields, you can also run conversion functions against the data in a Memo field. Number. You can enter only numbers in this type of field, and you can perform calculations on the values in a Number field. DateTime. You can enter only dates and times in this type of field. Depending on how the database designer sets the field, you may encounter these conditions If the database designer set an input mask for the field a series of literal and placeholder characters that appear when you select the field, you must enter data in the spaces and the format that the mask provides. For example, if you see a mask such as MMMDDYYYY, you must type a date in that format in the spaces provided for example, Oct 1. You cannot type a full month name such as July, or a two digit year value. If the designer did not create an input mask to control how you enter a date or time, you can enter the value using any valid date or time format. For example, you can type 1. Oct. 2. 00. 6, 1. October 1. 1, 2. 00. The database designer might apply a display format to the field. In that case, if not input mask is present, you can enter a value in almost any format, but Access displays the dates in accordance with the display format. For example, you can type 1. Oct 2. 00. 6. For more information about input masks, see the article Format data in rows and columns. Currency. You can enter only currency values in this type of field. Also, you do not have to manually enter a currency symbol.